If you’re building a new home or completing major renovations to your existing home, it’s important for you to understand the R value for insulation. This legal requirement ensures that your home meets the minimum energy efficiency standards, by keeping as much heat as possible inside during winter, and expelling as much heat as possible during summer. Insulation can have a big impact on this, which is why the R value system was created in the first place.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through what R value is for insulation, how it’s calculated, and the “best” values for your home’s ceiling. This will give you a good overview of why your home’s insulation is important, and will help you to make good decisions about your build or renovation.
What is R value for roof insulation?
R value is the thermal rating of insulation, which measures its ability to resist heat flow. It ranges from 1.5 to 7, with the higher end of the scale meaning greater heat flow resistance, and better insulation.
New Australian homes must meet a minimum R value depending on their climate zone (more on this below), which is outlined by the Building Code of Australia (specifically part 3.12 of the Building Code of Australia Housing Provisions, and AS/NZS 4859.1). One of the main reasons for this is to reduce the amount of energy that people use for their heating and cooling, which relieves stress on the national energy grid, reduces the need to burn more fossil fuels, and also helps to keep vulnerable people safe. If a home doesn’t meet the minimum R value based on their state and other building-specific requirements, a Certificate of Compliance (COC) cannot be issued, which means it can’t be legally occupied. This obviously isn’t the case for older homes without insulation because people are already living in them.
There are three types of R-value for insulation:
- “Up” R value (also called winter R-value) = the material’s resistance to heat flow out of the building
- “Down” R value (also called summer R-value) = the material’s resistance to heat flow into the building
- Total R value = the total resistance to heat flow from the roof and ceiling. Each material has its own R value, and the total is calculated by adding them together. These give the best measurement of performance and are the ratings that are used to measure total thermal efficiency in a home.
The goal of any type of house insulation (in the roof or otherwise) is to prevent heat from escaping in winter, and to deter heat from entering the home in summer. These are the typical heat losses and gains in a temperate Australian climate:
Image from Yourhome.gov
As you can see, a lot of heat is lost and gained through your ceiling, which can make big differences in your energy bills. According to the diagram from Your Home, a house loses about 35% of its heat through the ceiling, and installing roof insulation can save up to 45% on heating and cooling costs.1 Considering that heating and cooling are often the biggest items on your energy bill, the savings can be huge, which is why some people ask their builders to install insulation with higher R-values than are required, to create a more energy-efficient home (although this isn’t always the case, and there can be diminishing returns. The best thing to do is speak to your builder or roofer about this).
When it comes to insulation in Australia, there are two main types:
- Bulk insulation: these look like sheets of wool, and are made of materials like glass wool, natural wool, polyester, cellulose fibre and recycled paper. They work by trapping air inside millions of bubbles inside the material, which resist the flow of heat. They are the most common form of insulation for roofs.
- Reflective insulation: these are layers of aluminium foil laminated onto plastic or paper. They work by reflecting the heat of the sun and are more suitable for sunny climates like North Queensland.
It doesn’t really matter whether you get bulk insulation or reflective insulation. All that matters is that the minimum R value is achieved to satisfy the Building Code of Australia. Once insulation is installed, it typically lasts for decades, deteriorating very slowly over time. Most brands offer a 30-50 year guarantee.
The R values in Australia are metric and completely different to the values used elsewhere in the world, such as the UK or America. They can’t be converted either because the systems themselves are different.
How is insulation R value calculated?
R-value is calculated based on the thickness of the insulation, and its thermal conductivity. The formula is thickness (m) / thermal conductivity (W/mk). The thicker the insulation and the lower its thermal conductivity, the stronger its insulating power.
Insulation R value chart
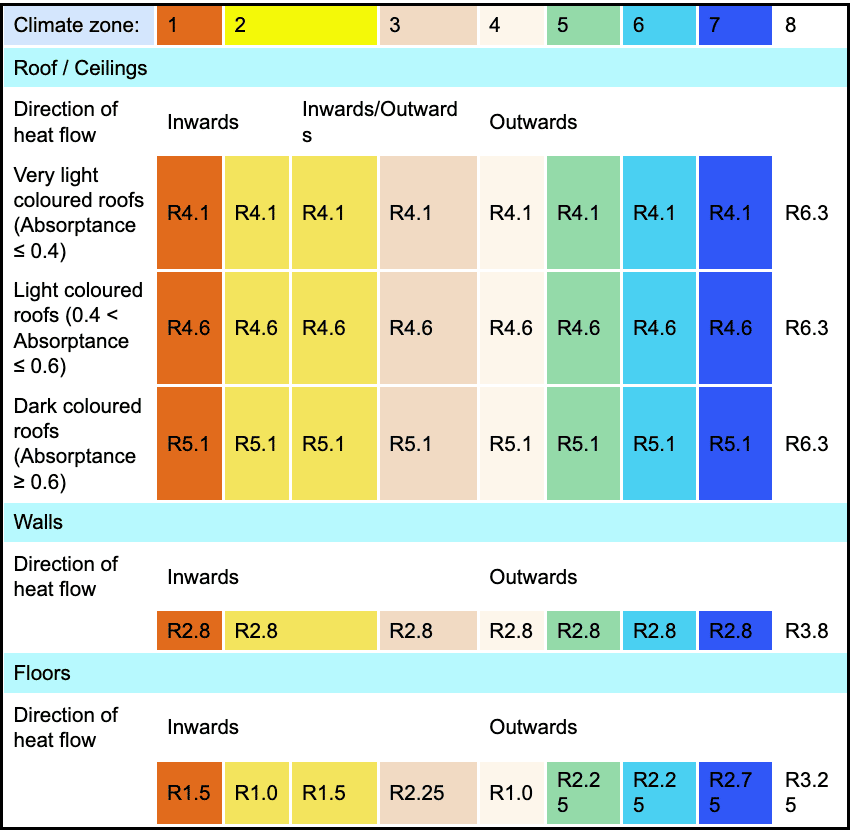
The insulation R value requirements are set by the Building Code of Australia, and are split into 8 separate zones as shown below. As you can see, the hottest parts of the country start at zone 1, and slowly increase to zone 8 the colder it gets.
Image from No Gap Insulation
However, finding the required R value for insulation isn’t as easy as simply selecting a zone. It’s also affected by the following:
- The construction of the home, considering elements like brick walls, windows, joists, and other thermal bridges (thermal bridges are places where heat can easily pass along)
- The colour of the home. Lighter colours reflect sunlight, and darker colours absorb it. That’s why it isn’t a good idea to have a black roof in sunny states like Queensland or the Northern Territory. They can get incredibly hot, which makes air conditioning work much harder, and cost a lot more.
- The home’s elevation above sea level. The higher you go, the colder it gets, and this is considered in a home’s required R value rating for insulation.
Here is a table from the Building Code of Australia that outlines the basic R value requirements for walls, roofs, and floors. But it’s crucial to understand that all of the above factors will affect the required R value for a particular home.
In addition to understanding the R value for a home, the builder or roofer installing the insulation must follow the manufacturer’s specs and instructions exactly to achieve the correct R values. It’s a combination of things that must be achieved correctly to receive the Certificate of Compliance.
Best R value for ceiling insulation
Insulations with higher R values have greater thermal resistance, but that doesn’t necessarily mean they will be better for your home’s unique build. To start with, they tend to be thicker than insulation with lower R values, which may make your roof space difficult (or impossible) to navigate because they start to cover joists. They are also more expensive, and you may not get enough savings on your energy to justify the costs. Ultimately, the best thing to do is talk to your roofer or builder and get their recommendation on the best R value for your ceiling insulation. If they know their stuff, they will be able to give you good advice.
References
- Insulation, YourHome